Omar Gadir, Ph. D., Founder/CEO, Iteru Systems
 Source Of Unstructured Data
Source Of Unstructured Data
Unstructured data could be generated by machines (machine-made data) or by humans (man-made data). Machine data, is generated by sensors, mouse clicks and similar sources. It contains information about the activities and behavior of customers, transactions, servers, network, mobile devices, smart meters, log files and weather. Data generated by humans is created on a daily bases and contains the vital business information: interaction between employees, contracts, design, strategies, manuals, compliance documents, research, product development, marketing data, etc.
During the last few years, the focus of new products has been on machine data which is broadly described as unstructured. Many articles, blogs and discussions give the impression that machine data represents all unstructured data, which is not true. As an outcome, man-made data has been ignored, although it is voluminous and it contains valuable information. In Iteru, we believe that both machine-made and man-made data are important. To stress the importance of man-made data I decided to write this blog.
Types of Data
There are two main types of data: structured and unstructured. Structured data refers to information with a high degree of organization, such that inclusion in a relational database is seamless. It is easy to extract information from structured data using data mining tools. Unstructured Data refers to information that does not have a pre-defined data model. This results in irregularities and ambiguities that make it difficult to extract information using data mining tools. Experts estimate that 80 to 90 percent of the data in any organization is unstructured and is growing significantly, many times faster than structured data.
There is also what is called semi-structured data. It is a form of structured data that does not conform with the formal structure of data, associated with relational databases or other forms of data tables, but nonetheless contains tags or other markers to separate semantic elements and enforce hierarchies of records and fields within the data. It is also known as self-describing structure. Types of Semi-structured data include: emails, XML and JSON. For the rest of this document semi-structured data is considered as a part of unstructured data.
Machine-made data
Machine-made data is purely textual and has a simple pre-defined format. In most cases it consists of delimited fields, for instance fields separated by commas, (CSV), or space, as shown below. For this reason it is easy to parse and extract columns. Machine data, mostly, is discarded after processing.
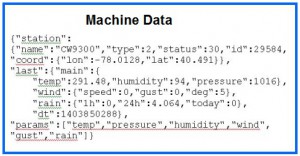
Man-made data
Man-made data has a complex formats. Mostly, man made data is perpetual, or is stored for a long time. It is much more difficult to parse and process for the following reasons:
Irregular structure: Examples of documents with irregular structure are: MS Word, PPT, PDF, Audio, Video, etc.
Proprietary government and industry-based formats: Examples of proprietary formats are: semiconductor industry “Standard Test Data Format (STDF)”. In pharmaceutical industry they use FASTQ format to store a biological sequence (usually nucleotide sequence). Examples of the government’s formats are: Seismic data format, GenBanks format (sequence database).
Includes thousands of metadata that contain vital information: for instance, a PDF automatically generates metadata that describes what changes and functionality are allowed within the PDF, if a password, certificate, or security policy has been applied to the PDF etc. There are some products that extracts text from PDF, ignoring the important metadata.
Embedded documents: For instance, an MS Word document may include reference to an Excel document, which in turn includes another reference to a PDF document.
As an example of the complexity of man-made data, below is the format of a PDF file
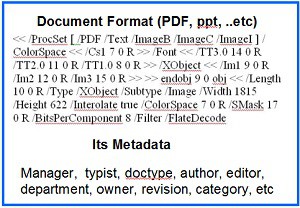
Current Analytics Solution
Most, if not all, analytics products (Tableau, Platfora, Datameer and open source visualization/analytics tools) deal with three unstructured data types: flat files (CSV), Excel and JSON. This constitute 3 data types of unstructured data out of more than 400 data types, which is less than 1% of the total number of data types. Virtually all of remaining 397 types are man-made.
To run analytics data should be transformed into flat files, Excel and JSON using data extraction and data mining algorithms. In many cases the algorithms have the following limitations:
- Data processed is of poor quality that leads to inaccurate analytics.
- Cannot deal with dynamic data, when data changes algorithm should be executed again.
- Extremely difficult to integrate conflicting or redundant data from different sources and formats, for instance, multimedia files (audio, video and images), geo data, text, social, numeric.
- Are not efficient or scalable.
For this reasons, data mining algorithms have rather limited success when processing unstructured data, in particular man-made data. Perhaps this explains why 80% of the unstructured data is not processed (dark data). Concerning structured data, the data mining algorithms have much better success.
Unified Solution for Man-made and Machine-made Data
In Iteru, we believe both man-made and machine-made data are important. It developed algorithms to deal with the four problems covered in the previous section. Its solution is based on the following:
- Data cleansing.
- Ability to deal with dynamic data.
- Process all 400 types of unstructured data.
- Efficient and scalable solution.
Iteru analytics and visualization tools covers all types of unstructured data. It processes all unstructured data and presents results in a tabular form which is amenable for processing by Iteru’s analytics tools and third party tools (Tableau, Platfora, Datameer and open source visualization/analytics tools).
